Motivation
Modeling infectious diseases helps us improve our understanding of certain characteristics such as the speed with
which it can spread in a population, the critical immunization threshold needed for it to die out or the
number of deaths that can be expected from an epidemic.
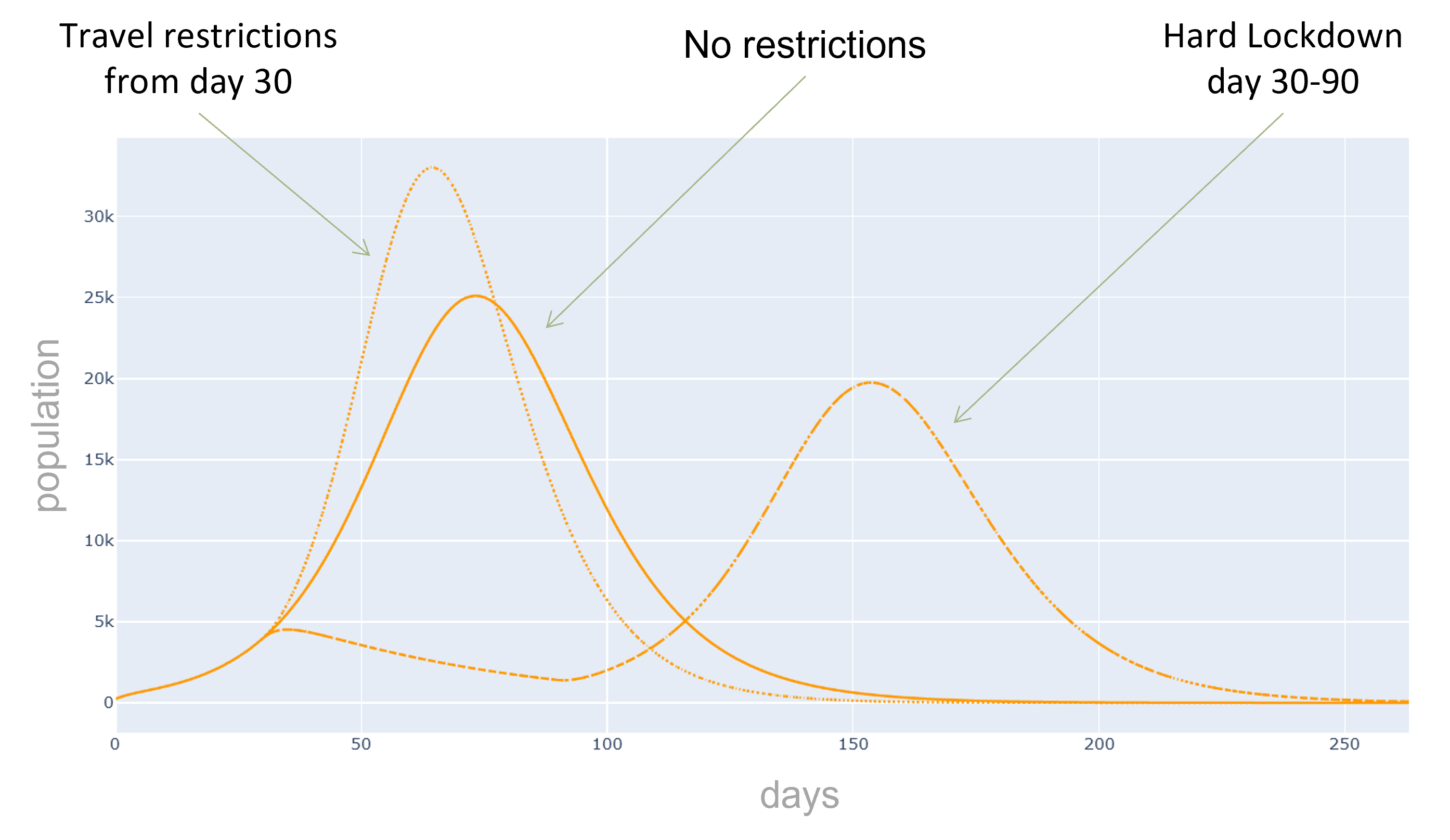
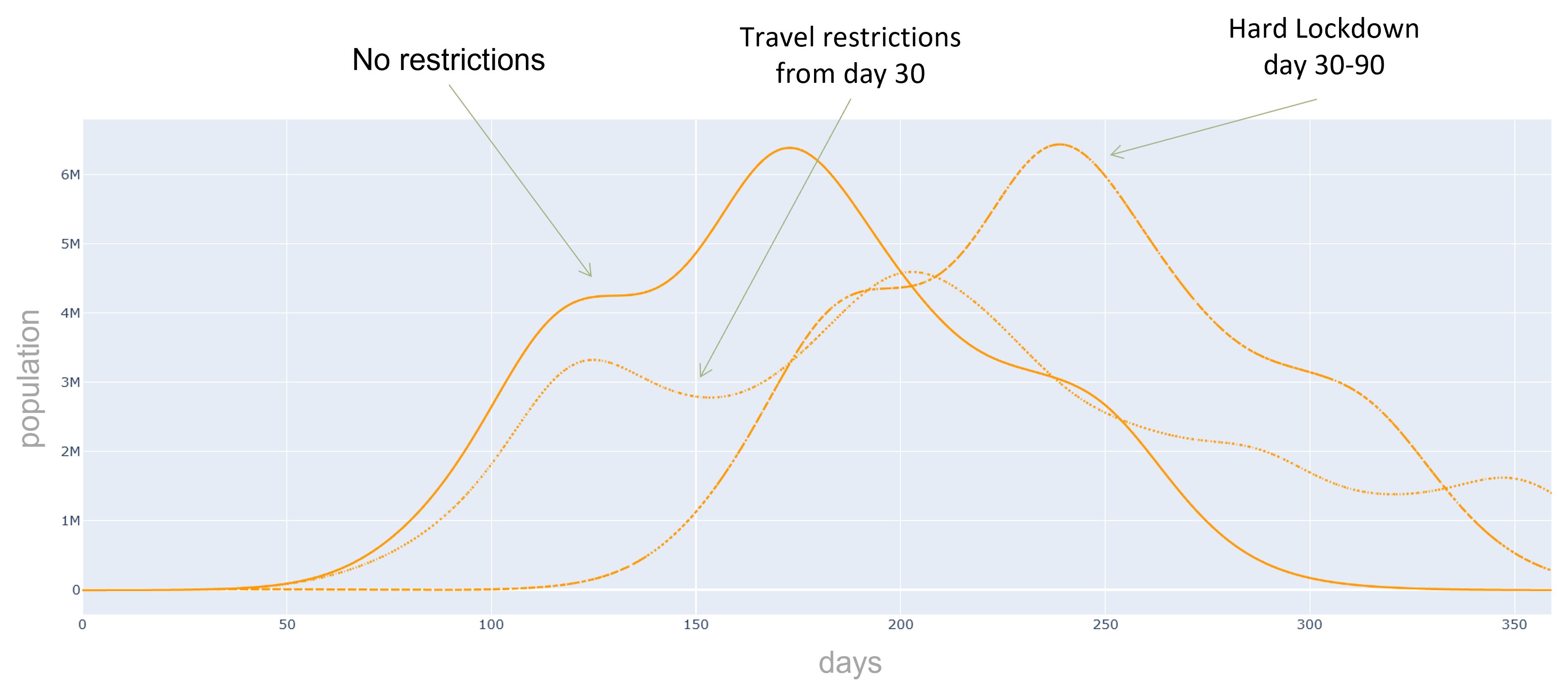
Additionally, we can evaluate the effectiveness of preventive measures such as quarantines, contact and travel
restrictions or targeted vaccination campaigns.
Models generally only represent a simplified view of the often complex real-world situation, where the spread of
a disease can be influenced by a populations age, the economic wealth of a region, the complex web of cantact
between individuals or seasonal variations. Especially in the case of new viruses such as Covid-19, many values
needed for accurate modeling are yet unknown due to a lack of data. Even though it might be possible to fit the
parameters of a model to the known data of a disease, the correctness of these parameters can not be guaranteed.
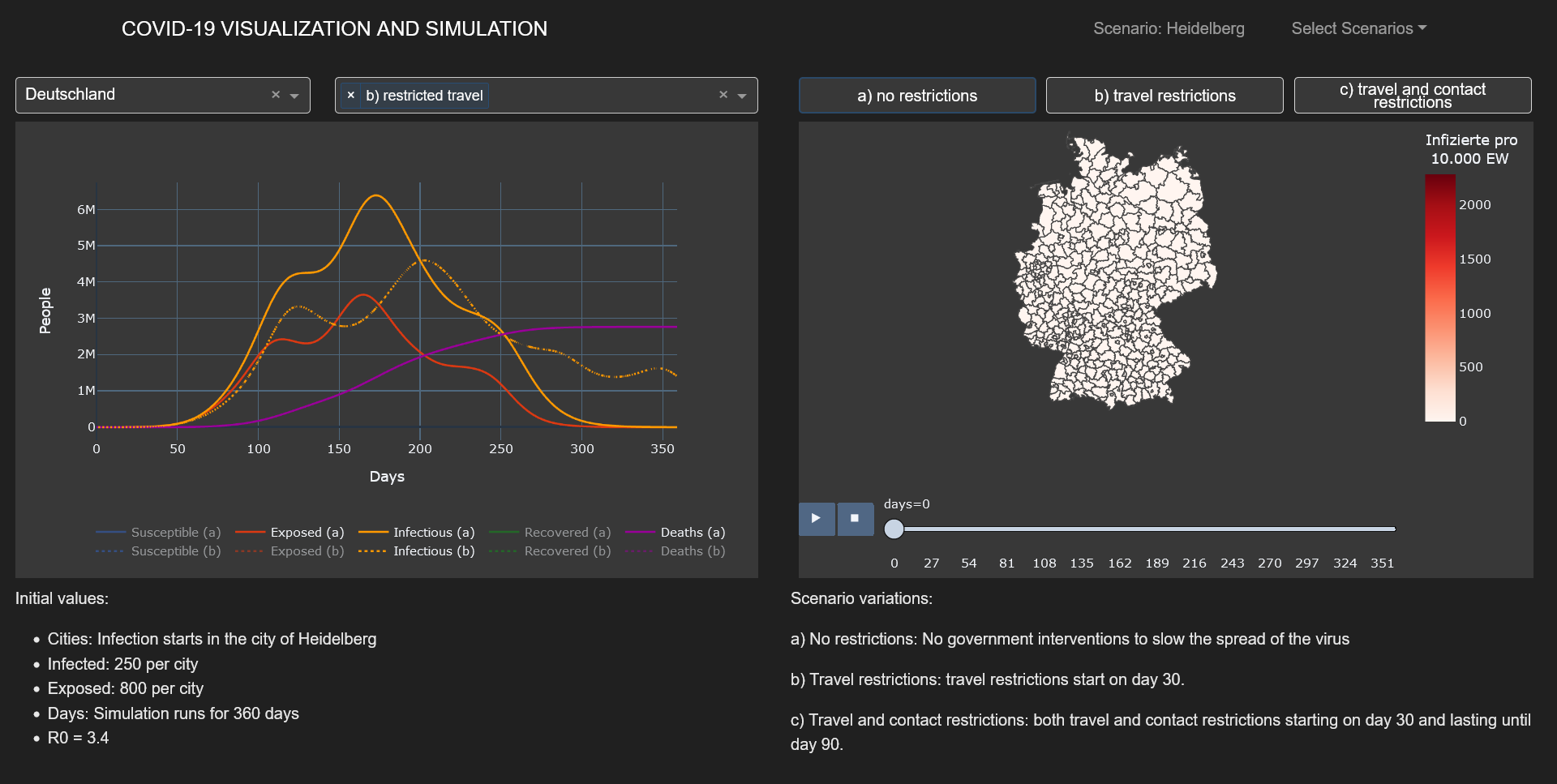
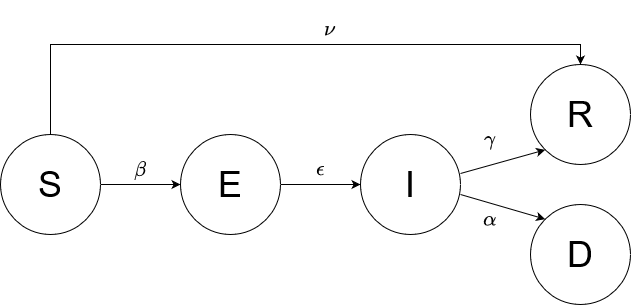
In this practical project, a SEIRD compartment model is used to evaluate the spread of an infectious disease
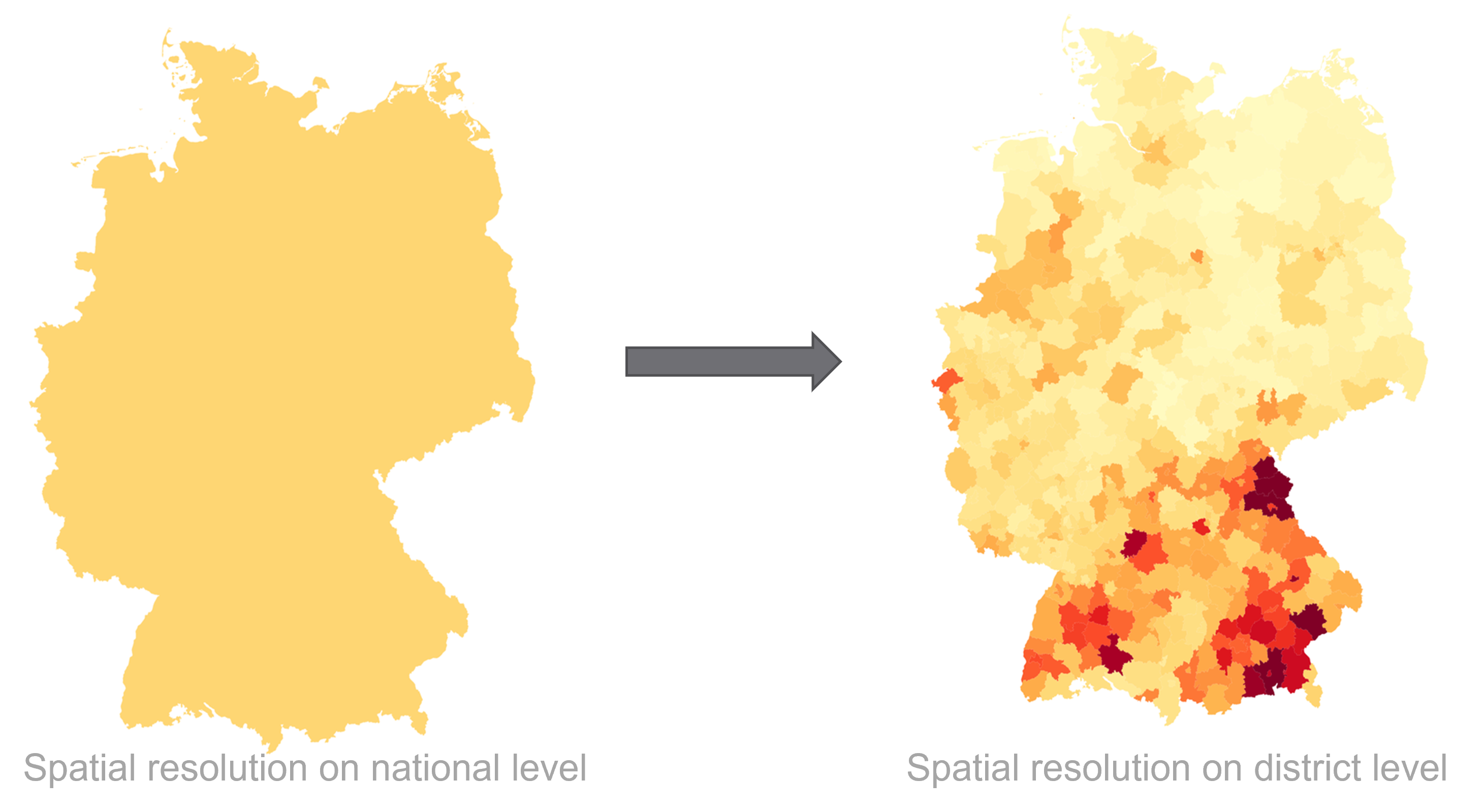
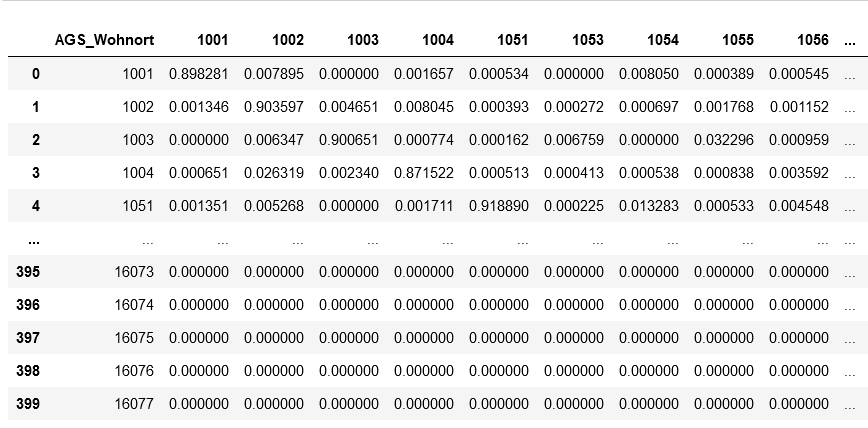
using the example of Covid-19. In addition to the temporal aspect of compartment models, a spacial aspect is
added by incorporating interregional commuters into the model. The results of the model were animated and a
dashboard was implemented for presenting the visualized results.
The implemented model as well as the results are discussed in the following sections.
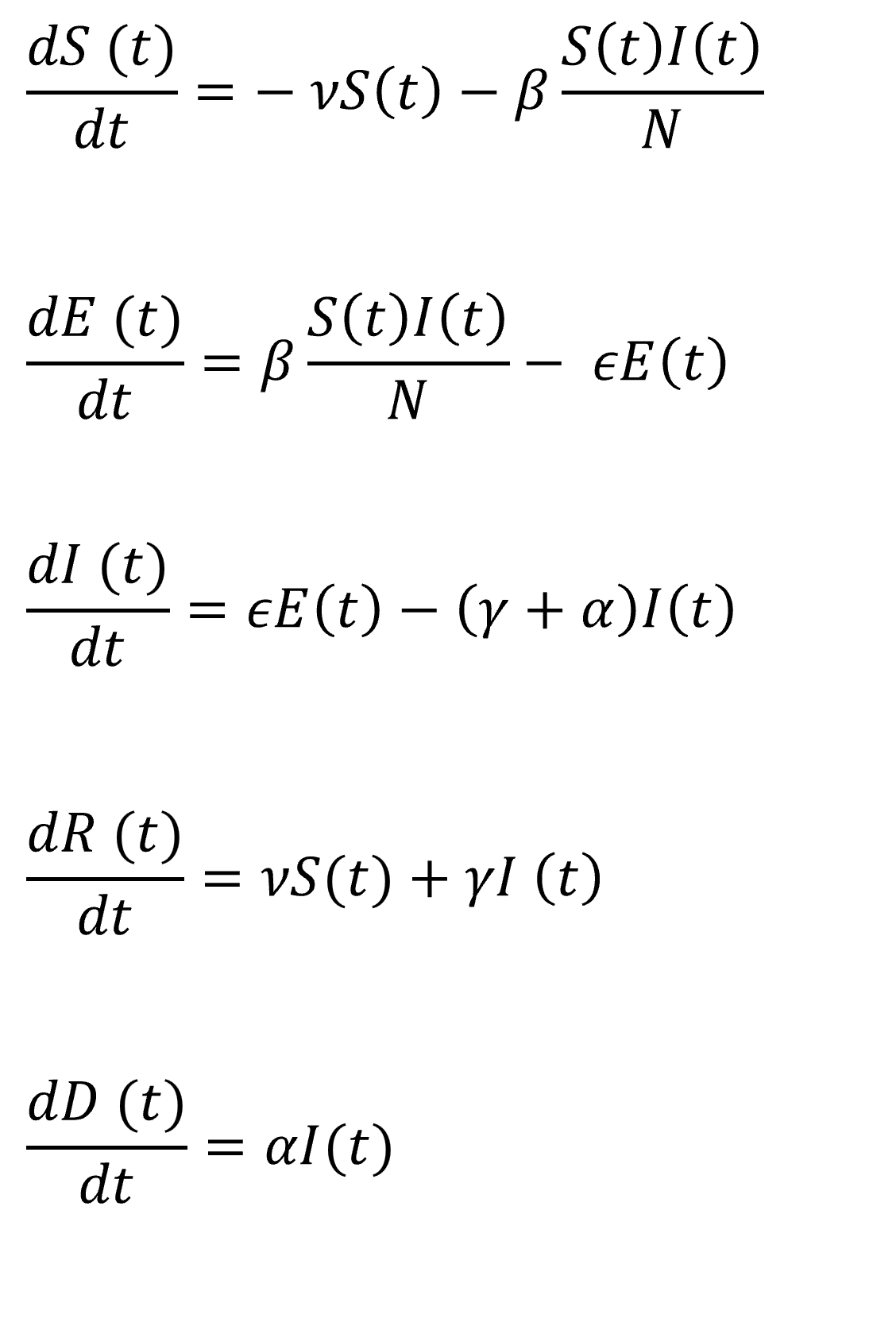
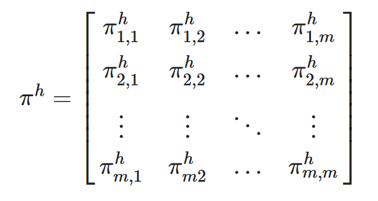
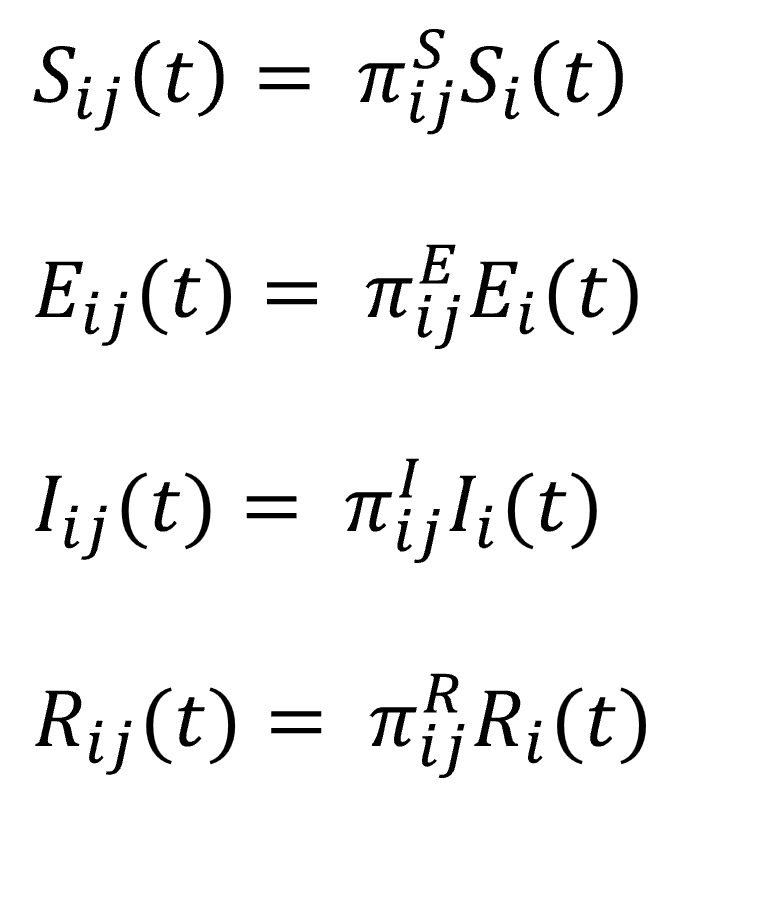
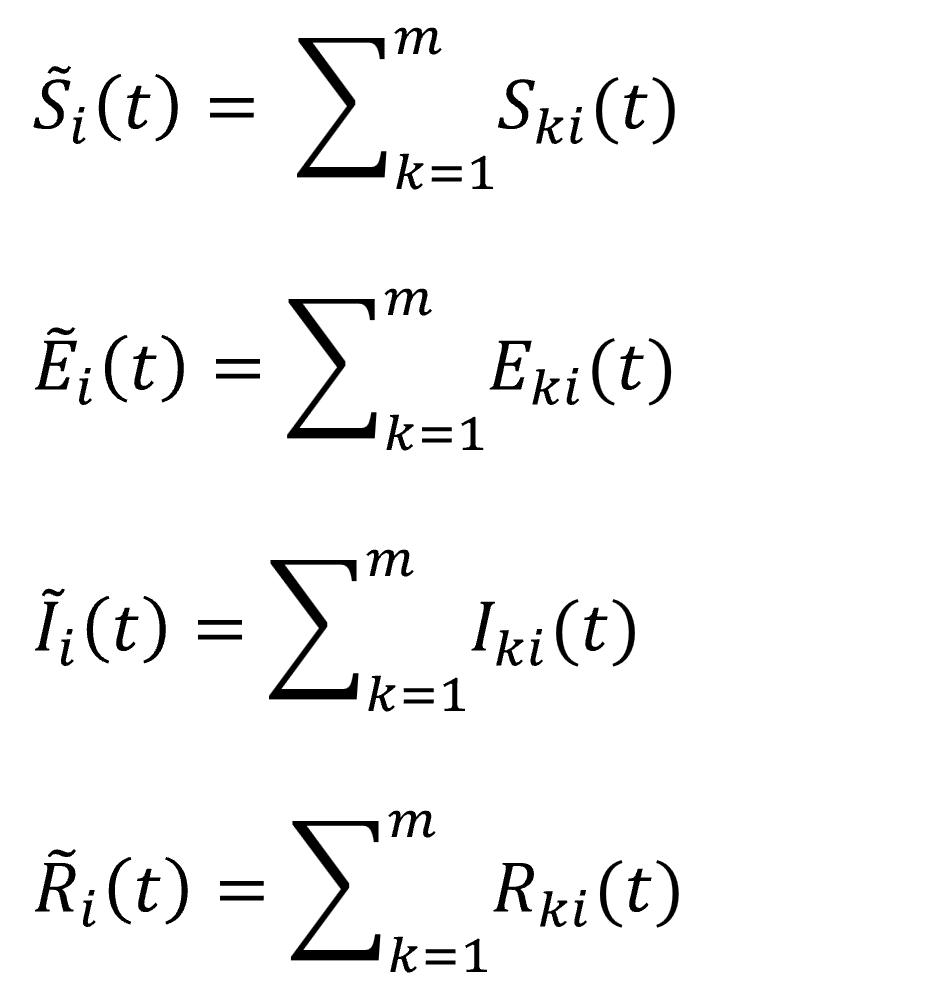
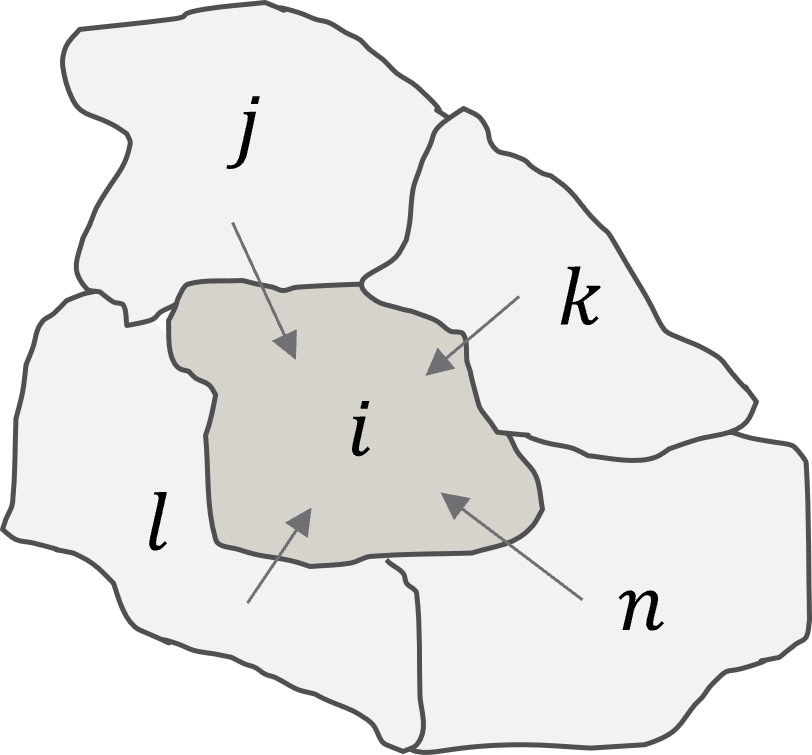


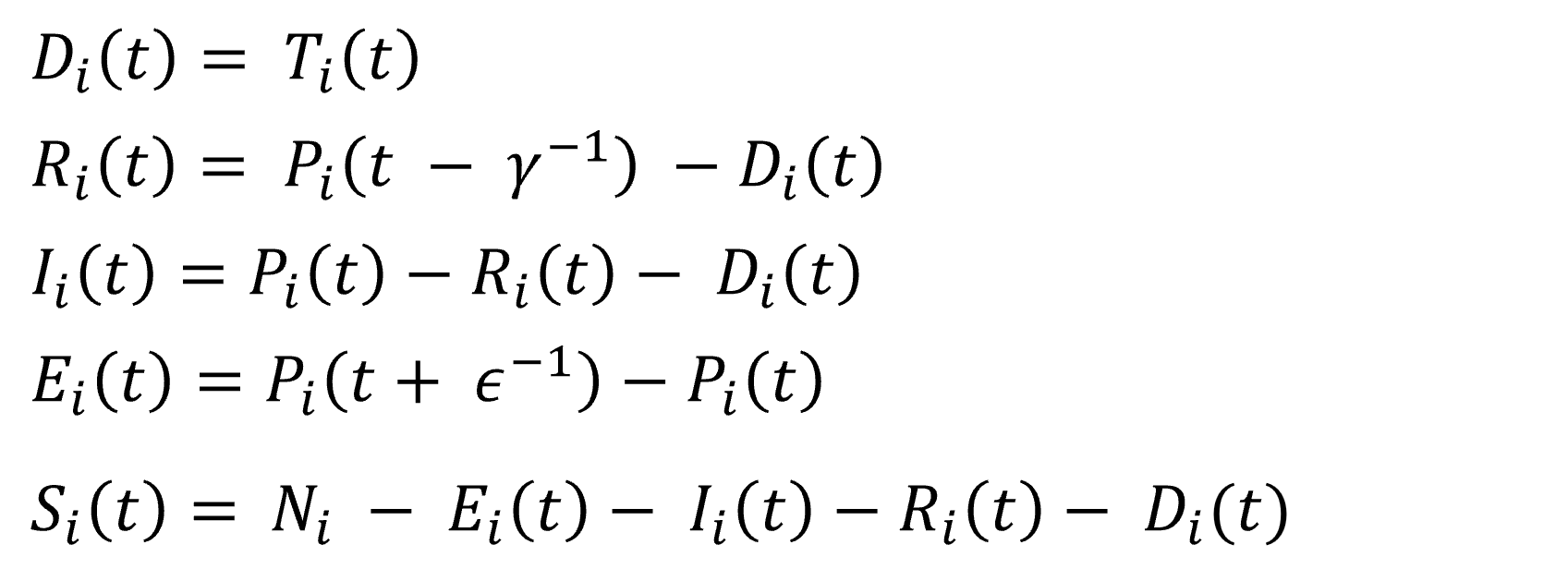 ,
,
 ,
,
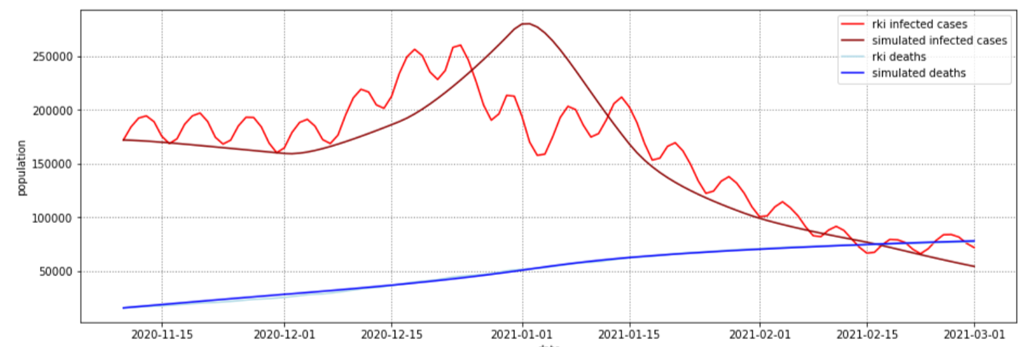 ,
,
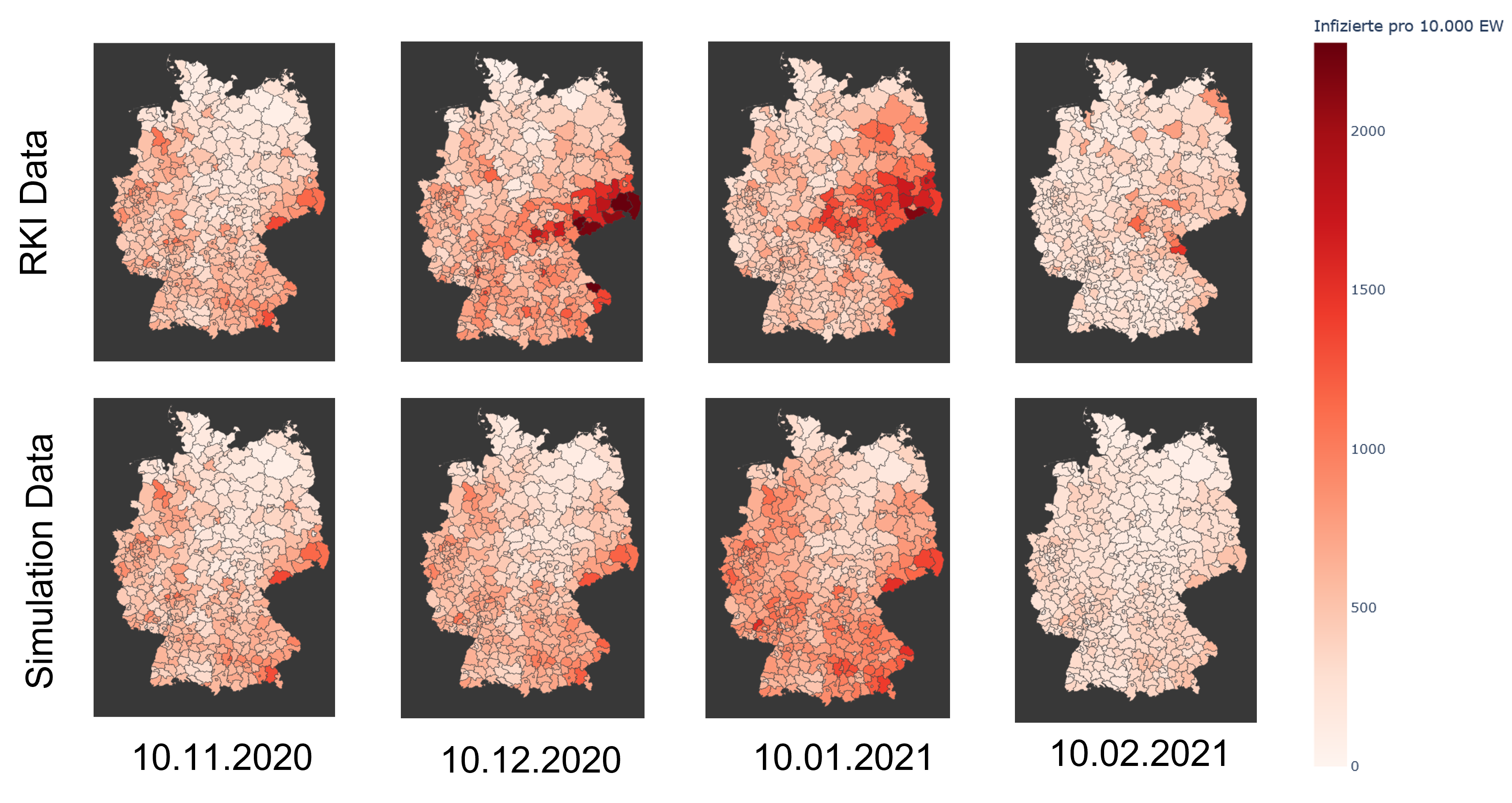 ,
,
 ,
,